Faster mobile connections and better coverage arrive in Torrevieja with the 4G and 5G deployments. Arrive700 helps the user in incidents with DTT
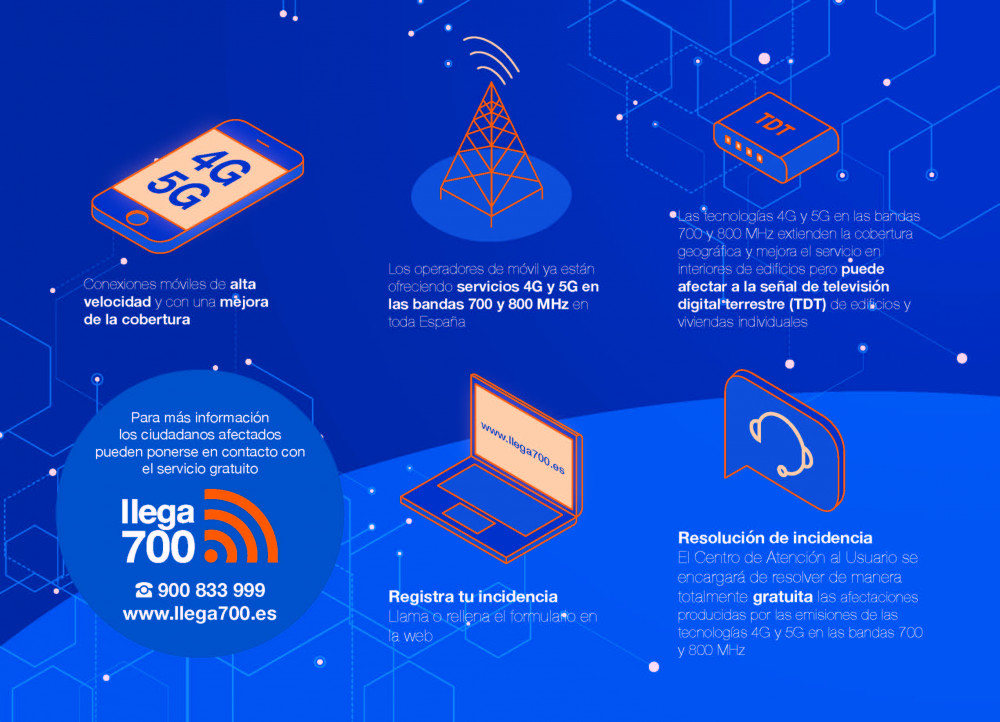
- Mobile phone operators begin to offer new generation mobile services in Torrevieja, 4G and 5G, in the 700 and 800MHz bands.
- The new technology will allow the people of Torrevieja to enjoy high-speed mobile data services, will improve coverage inside buildings and will expand the geographical area.
- Arrive700 is the entity in charge of guaranteeing the compatibility of this service with DTT
The mobile telephony operators, Telefónica, Vodafone and Orange, have announced that during the next few weeks they will carry out in Torrevieja the process of implementing new generation mobile telephony services, 4G and 5G, on the 800 and 700 MHz bands, respectively , which will allow Torrevejenses to enjoy high-speed mobile connections with better coverage inside buildings and greater geographical extension.
To guarantee the compatibility of the new technology with digital terrestrial television (DTT), Arrive700 is the entity launched by the operators to solve any affectation in the reception of the television signal.
The implementation process is being carried out gradually throughout the national geography. To check if these services are already active in Torrevieja (or any other location), you can consult the following link: https://www.llega700.es/contacto_mapa.php
The deployment is part of the provisions of Royal Decree 579/2019, of October 11, from which the frequencies between 694 and 790 MHz (channels 49 to 60 of UHF) that were used until then were released. for the reception of Digital Terrestrial Television, a process also known as the Second Digital Dividend. From then on, these frequencies were assigned to mobile phone operators to provide their new generation mobile phone services.
Main advantages: more and better coverage
With the new mobile network, the door has been opened to innovative services and applications, in addition to providing significant improvements in both download speed and data sending (photos, music or high-definition audiovisual content) or allowing you to get the most out of to online applications, such as video games.
The new generation mobile phone network introduces two fundamental improvements. The first is the solvency of the various problems related to complicated orographies present in the Spanish geography where coverage traditionally failed. The second is the great penetration in interior areas of buildings.
The new generation also facilitates the introduction of new services in the business area and public administrations, such as mobile business applications with high multimedia content or the use of video calls, among others.
In addition, the greater coverage achieved by the deployment in the 700 and 800 MHz bands will improve the service inside buildings and will be the band that allows the service to be extended geographically efficiently.
Guaranteeing the compatibility of the new generation mobile network and DTT
Arrive700 is the managing entity in charge of offering the services that will guarantee compatibility between the start-up of 4G and 5G mobile broadcasting in the 800 and 700 MHz bands, respectively, and the reception of the DTT service.
In order to guarantee this compatibility, Arrive700 provides citizens with a series of free services that includes a corrective procedure after the stations are turned on, for which Arrive700 will be in charge of attending to the affected users, managing and resolving possible damages at no cost.
To manage these services, a free phone number (900 833 999) and a website www.llega700.es have been made available to citizens.
State of the art regarding the microbiota in hypersaline media
University of Alicante, October 2021
NOTE: the original work in English was carried out by a team (see Author Contributions, under these lines) led by Ms. Rosa María Martínez Espinosa, Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Department of Agrochemistry and Biochemistry (Faculty of Sciences) and Multidisciplinary Institute for the Study of the Environment "Ramón Margalef" University of Alicante, Ap. 99, E-03080 Alicante. IP research group "Applied Biochemistry".
Hypersaline ecosystems are environments in which the concentration of salt present in the water or in the soil is about 10 times higher than seawater (the average salt content in seawater is 35 grams/litre, while in hypersaline ecosystems such as the Dead Sea can reach 337 grams/litre). These ecosystems can be coastal or inland systems, being able to find salty lakes or lagoons, salt pans for salt precipitation (coastal or inland), marshes, saline diapirs, etc.
Traditionally, hypersaline environments have been valued for their landscape characteristics, for being habitats for a large number of animal species (particularly migratory birds or small crustaceans), for mining exploitation that can be carried out in many cases (extraction of sodium chloride mainly for human consumption roads, food processing or cosmetic production, among other uses), or for its tourist value (salt crust baths, buoyancy in hyper-salty water from the Dead Sea, therapeutic mud baths, etc.).
At the end of the 1970s in the 20th century, advances in microbiology, biochemistry and molecular biology techniques and protocols allowed the development of studies in which new microbial species began to be isolated and characterized from environmental samples of all kinds. These studies gave rise to a new way of understanding nature and confirmed that microbial diversity is much broader than initially suspected. Hypersaline environments were not immune to this phenomenon and from then until now, the investigation of the microbial biodiversity of these hypersaline ecosystems constitutes a field of action of great interest worldwide. This interest is based above all on the fact that many of the microorganisms that inhabit these media have peculiar characteristics that allow them to live in the presence of high concentrations of salt. Thus, their metabolism and certain molecules they synthesize are of great interest for industrial processes and biotechnological applications.
The impact of these biotechnological applications (production of bioplastics, pigments, antibiotics, removal of heavy metals, etc.) is such that more and more studies are exploring and describing for the first time hypersaline environments not studied molecularly until now, with the objective of characterizing the microbial biodiversity that inhabits them and determining possible applications of the species present there or the molecules they produce.
In this context, hypersaline environments such as the Laguna Rosa de Torrevieja, Laguna de la Mata, inland salt flats in the province of Alicante in the upper Vinalopó, etc. they are still poorly studied environments, despite the fact that they are known on a large scale due to their interest in mining exploitation to obtain salt.
This work aims to give visibility to the added value of these ecosystems (emphasizing the Laguna Rosa de Torrevieja), as natural sources of microorganisms with interesting applications in Biotechnology.
author contributions
Rosa María Martínez-Espinosa (RMME) conceived the global project and managed the financing. Guillermo Martínez (GMM) and Rosa María Martínez-Espinosa carried out the bibliometric and bibliographic analysis and integrated all the data into the local database. Carmen Pire (CP), GMM and RMME analyzed the results and contributed equally to the writing of the original draft, review of the results and final editing. All authors have read and accepted the published version of the manuscript.
Money
This work has been funded by the Torrevieja City Council and by a research grant from VIGROB-309 (University of Alicante)
Legal feasibility report and roadmap for the enhancement for therapeutic and cosmetic uses, of the brine and peloids of the Laguna Rosa and of sea water
The Torrevieja City Council is carrying out a series of actions whose objective is to enhance the value of the brine and sludge from the Laguna Rosa de Torrevieja and, as a complement and in connection with the above, of seawater. This action is preceded by the preparation of an Early Demand Map of needs for Public Procurement of Innovation, one of which is, precisely, the enhancement of natural resources.
The City Council has counted, as collaborating entities in the scientific and academic field, with the universities of Alicante, Complutense and Alcalá. Without a doubt, it will also require the assistance of other universities and technology and/or research centres. In this project, the City Council has the support of the Generalitat Valenciana, materialized with the financing of certain projects by the Valencian Innovation Agency (AVI) and the collaboration of different ministries and organizations of the Autonomous Administration.
The feasibility study and roadmap that makes it possible to value the brine and peloids from Laguna Rosa, and seawater, for therapeutic, cosmetic, biotechnological and other uses of potential interest has been carried out by a specialized team of the General Foundation of the University of Alcalá /FGUA). The purpose of FGUA's work is to explore the feasibility and roadmap for the enhancement of resources. Identifies and dissects the legal problems that the enhancement of resources hitherto barely explored or implemented in the Laguna Rosa and its surroundings in Torrevieja, may pose in order to address public policies and/or private activities necessary for such enhancement, given account of the existing conditions regarding the use and exploitation of the area and the regulations that govern access to said resources or their future exploitation.
The Roadmap exposes, therefore, the limitations that different state, regional and municipal regulatory groups, sometimes conditioned by international law and that of the European Union, offer for the possible enhancement of resources. None of the limitations is opposed to such enhancement but, rather, they must be seen as opportunities by directing the main attention towards biodiversity, including the biotic components (microorganisms) that inhabit the environment. The study has been approached thanks to a contract that is part of the project Impulse to Innovative Public Procurement (CPI-L2) Torrevieja Town Hall, co-financed by the European Union through the Operational Program of the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) of the Comunitat Valenciana 20142020 through the Valencian Innovation Agency (AVI).
Torrevieja Smart City Guide, October 2021
In the fall of 2021 and within the framework of an initiative promoted by the Alicante Provincial Council, the Valencian Association of the Energy Sector and the Smart Cities think tank, a dialogue process took place between numerous small, medium and large municipalities of the Valencian Community , councils, SMEs and large companies, technological institutes, universities and other agents.
The ultimate goal was to develop a Smart City guide for each of the participating municipalities. The work began by preparing a diagnosis of the current situation of the municipality and this according to the thematic blocks of the Spanish Network of Smart Cities (RECI). Short, medium and long-term challenges, opportunities and objectives were identified, as well as ongoing and/or projected initiatives. The departments and areas of the City Council of Torrevieja participated. Special attention was shown to data management.
For each initiative, three questions about "the data" were posed and answered: data generation and storage in a single repository, the data generated is/would be exploited in new initiatives or would provide feedback to the parent initiative, it was an initiative that contributes to generate Open Data... The Smart City Guide of the City Council of Torrevieja prepared in October 2021 is nothing but a working instrument where concrete initiatives are reflected, quantified their degrees of progress, and related both to challenges and to the great thematic areas in which the RECI cities structure their activity.
The Guide is not a Master Plan or a detailed action program nor is it an exhaustive document, but it is a still photo of reasonable quality that includes the initiatives that, in some way, characterized the smart city course in Torrevieja in autumn 2021.